+++ In response to numerous customer requests, we offer a one-day training "What's new in SAFe® 5.0?", which introduces and explains the innovations in detail.
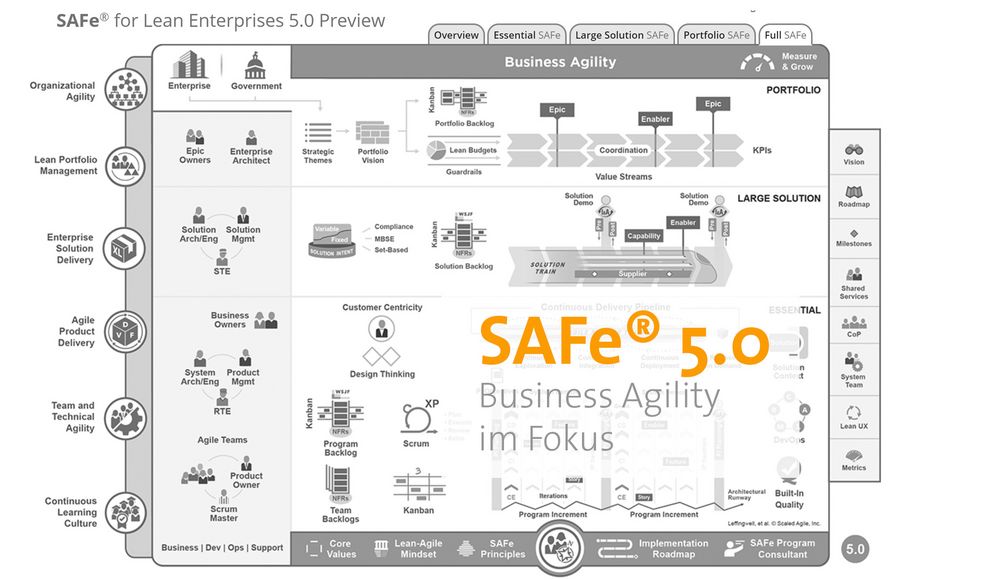
At the Global SAFe Summit in San Diego, Dean Leffingwell, founder of the Scaled Agile Institute SAI and publisher of the Scaled Agile Framework, announced the big news: From February 2020 onwards there will be a new Big Picture. The current SAFe® Version 4.6 has been revised, adapted and extended to enable the benefits of agility to be experienced even more holistically throughout the entire organization. In the following, we would like to demonstrate what the new features in SAFe® 5.0 will be, which topics have been revised and what changes will take place for companies in SAFe® 5.0.
Business Agility – What is it? Why SAFe® 5.0?
We started with agile methods in software development. Over time and with the corresponding sense of achievement, these practices and tools were tested in other industries and we are now using the Scaled Agile Framework in hardware development and embedded systems. In order to raise the value of agility holistically End2End, it should not be limited to the development organization. The greatest effect is achieved when the entire organization uses lean and agile practices to continuously and proactively deliver innovative solutions to customers faster than their competitors. This so-called Business Agility is now the focus of SAFe® 5.0, and the new version adds important elements that help to consolidate Business Agility throughout the entire company and clearly places its customers in the center. For this reason, the Big Picture has been supplemented by several elements that are now displayed one after the other.
The structure of the 4 configurations: Essential, Large Solution, Portfolio and Full SAFe® remains basically the same. For better orientation please find the Overview TAB below, which describes the 7 core competencies, 2 more than in SAFe® 4.6.

The basis continues to be the competence Lean-Agile Leadership.
In this picture 3 core competencies are defined for execution and 3 for strategy. The Execution competencies are designed in two configurations:
The Execution competencies are designed in two configurations:
- Essential SAFe® where the separation of team and program level has been removed to emphasize collaboration between teams. In this way you have one level less of smiles :). On this new Essential level, the competencies "Team and Technical Agility" and "Agile Product Delivery" are included.
- Large Solution SAFe®is then used to scale solutions that go beyond a Train. In addition, there is the Competent Enterprise Solution Delivery.
The strategic competencies are required for 2 further configurations:
- PortfolioSAFe®, where competencies such as Strategic Portfolio Management and now Continuous Learning Culture and Organisational Agility are outlined.
- Full SAFe® then combines Large Solution and Portfolio for the maximum expansion level, as been done so far.
In general, the important core competences have moved to the left and the range of products to the right. All roles are coming together again and the customer moves towards the centre. Let's go through the new and restructured competencies one after the other:
1. Lean-Agile Leadership
Lean agile leadership competency describes how lean-agile leaders drive and support organizational change by empowering individuals and teams to reach their greatest potential. This results in dedicated employees, increased productivity and innovation, and successful organizational change.
Lean-Agile Leadership was divided into three dimensions:
Lead by example - Leaders deserve to be given authority by displaying the desired behaviours themselves, so that others are happy to follow them and set an example for their personal behaviour.
Mindset and Principles - By living the lean and agile way of working in their decisions, responses and actions, leaders influence the values and culture of the company.
Leading change - Leaders not only support but also lead the transformation by creating the right environment, motivating people and providing the necessary resources.
These changes also affect the well-known leadership artifacts - the principles and also the House of Lean were added:
SAFe® Principle #10 - Organize around value intends to lead companies to align their development on the complete, continuous value flow. SAFe®'s concept of value streams manages the people who need to work together, increases quality and minimizes delays and handovers.
The SAFe House of Lean chart has been updated to reflect the changes in the new and revised core competencies. Added are aspects such as from project focus to product focus, experiments and feedback or a culture of problem solving.
2. Continuous Learning Culture
This is the first of two completely new core competencies. It describes a set of values and practices that encourage individuals - and the company as a whole - to continuously increase knowledge, competence, performance and innovation.

This core competence is also expressed in three dimensions:
- Learning Organization - Employees on all levels learn and grow to allow the organization to change and adapt to an ever-changing world.
- Culture of innovation - Employees are encouraged and empowered to explore and implement creative ideas that enable future value creation.
- Continuous Improvement - Every part of the company focuses on the continuous improvement of its solutions, products and processes.
3. Team and Technical Agility
The Team and Technical Agility competency describes the critical skills and lean-agile principles and practices that high-performance agile teams and teams of agile teams use to develop high-quality solutions for their customers. The result is higher productivity, better quality, shorter time-to-market and predictable, reliable value creation.

This competence has been rewritten and is now divided into the following dimensions:
- Agile Teams - High-performing, cross-functional teams apply agile principles and practices every day.
- Team of agile Teams - Agile Teams work within a SAFe® Agile Release Train (ART), a long-standing team of agile teams working together with a common vision and direction.
- Built-in Quality - All agile teams use agile practices to develop high-quality, well-designed solutions that support current and future business needs.
Instead of a development team, SAFe® 5.0 now has a business team to illustrate that business agility happens on all levels of the organization.
4. Agile Product Delivery
The DevOps and Release on Demand competence has been renamed Agile Product Delivery, focusing more on a continuous value stream of products and services to customers and users. This competency enables the company to deliver solutions that excite customers, reduce development costs, mitigate risk and outperform the competition.

This core competence also comprises three essential aspects:
- Customer Centricity and Design Thinking - Customer focus puts the customer at the centre of every decision and uses design thinking to ensure that the solution is desirable, feasible, practical and sustainable.
- Develop on Cadence; Release on Demand - Developing on Cadence helps to manage the variability associated with product development. Decoupling the value chain ensures that customers get what they need, when they need it.
- DevOps and the Continuous Delivery Pipeline - DevOps and the continuous supply pipeline create the foundation that enables companies to meet customer and market demand at all times.
Moreover, two important elements were introduced into the Agile Release Trains:
- Design Thinking
Design Thinking represents a fundamentally different approach to product and solution development, in which certain creativity techniques are applied in multidisciplinary teams to understand a problem, design a solution and bring that solution to market. It is always important to look at things from the user's perspective, which is also reflected in the element "Customer Centricity". - Customer Centricity
This demonstrates that it is not only important HOW something is developed, but also WHAT is developed. The basis for action should be thorough market research and a real understanding of user needs. The core competencies 1,3 and 4 are now combined in the Essential SAFe® - no more separation between team and program level.
5. Enterprise Solution Delivery
Lean Systems Engineering became the competence Enterprise Solution Delivery. This competence describes how to apply lean-agile principles and practices to the specification, development, deployment, operation and development of the world's largest and most demanding software applications, networks and cyber physical systems.

Its guidelines are as follows:
- Lean Solution and Systems Engineering covers all activities necessary to specify, design, implement, test, develop and finally commission large systems.
- Coordinating Trains and Suppliers coordinates and aligns the extended and often complex value streams towards a common business and technology mission. Important here are a coordinated vision, backlogs and roadmaps with common Program Increments (PI) and synchronization points.
- The continuous development of live systems ensures that large systems and their development pipeline support the principle of continuous improvement.
6. Lean Portfolio Management
Lean Portfolio Management wendet lean- und Systemdenken auf Strategie und Investitionsfinanzierung, Agile Portfolio Operations und Governance an. Diese Kooperationen geben dem Unternehmen die Möglichkeit, die Strategie wirklich umzusetzen, bestehende Verpflichtungen zuverlässig zu erfüllen und Innovationen besser zu steuern.

- Strategy & Investment Funding stellt sicher, dass das gesamte Portfolio ein Alignment findet und finanziert wird, um die Produkte und Services zu schaffen und zu erhalten, die zur Erreichung der Geschäftsziele erforderlich sind.
- Agile Portfolio Operations koordiniert und unterstützt die dezentrale Programmausführung und fördert die operative Leistungsfähigkeit.
- Lean Governance ist die Überwachung von Ausgaben, Audit und Compliance, Forecast und Metriken.
7. Organizational Agility
Ganz im Sinne Business Agility beschreibt die letzte Kernkompetenz Organizational Agility, wie lean denkende Menschen und agile Teams ihre Geschäftsprozesse optimieren, Strategien entwickeln und die Organisation bei Bedarf schnell anpassen, um neue Chancen zu nutzen:

- Lean-thinking People und agile Teams - Alle an der Leistungsbereitstellung Beteiligten sind in Lean and Agile Methoden geschult und verkörpern die Werte, Prinzipien und Praktiken.
- Lean Business Operations - Teams wenden lean Prinzipien an, um die Geschäftsprozesse, die die Produkte und Dienstleistungen des Unternehmens unterstützen, zu verstehen, abzubilden und kontinuierlich zu verbessern.
- Agile Strategie - Das Unternehmen ist agil genug, um den Markt kontinuierlich zu erfassen und die Strategie bei Bedarf schnell zu ändern.
Die vorgestellten Erweiterungen und neuen Elemente, wie z.B. die zwei Core Competencies der lernenden Kultur und Business Agility, Design Thinking mit dem klaren Kundenfokus oder das Ersetzen der IT-fokussierten Entwicklungsteams durch Business-Teams zeigen ganz klar, wie sich das gesamte Framework auf allen Ebenen auf Business Agility ausrichten soll.
SAFe®definiert Business Agility als:
„die Fähigkeit, im digitalen Zeitalter wettbewerbsfähig und erfolgreich zu sein, indem man schnell auf Marktveränderungen und sich bietende Chancen mit innovativen Geschäftslösungen reagiert. Es erfordert, dass alle, die an der Bereitstellung von Lösungen beteiligt sind - Geschäfts- und Technologieführer, Entwicklung, IT-Betrieb, Recht, Marketing, Finanzen, Support, Compliance, Sicherheit und andere - Lean- und Agile-Verfahren anwenden, um kontinuierlich innovative, qualitativ hochwertige Produkte und Dienstleistungen schneller als der Wettbewerb bereitzustellen.“
Damit die Fortschritte der Transformation zu einem „agilen Business“ auch objektiv messbar sind, gibt das neue Big Picture in der Version 5.0 auch gleich noch hilfreiche Kennzahlen an die Hand. Portfolio Manager und das Lean-Agile Center of Excellence (LACE) haben nun die Möglichkeit, ihre Fortschritte auf diesem Weg selbst zu bewerten. Die Konsequenz aus dem erweiterten Big Picture ist nun natürlich auch, dass die Einführung von SAFe® etwas umfangreicher sein kann. Um die Veränderungen in den Kontext einer Transformation einordnen zu können, wurde auch die Implementation Roadmap adaptiert. Die Trainings zu Lean Portfolio Management (LPM) und Agile Produkt- und Lösungs-Management (APSM) ergänzen die bekannte Journey um wertvolle theoretische Inhalte auf dem Weg zur Business Agility.

Doch was bedeutet SAFe® 5.0 für mich als Anwender?
- Wenn Sie noch keine Zertifizierungen mit SAFe® gemacht haben, so können Sie ab Februar ganz normal eines unserer Trainings besuchen. Sie finden eine ausführliche Liste mit den verschiedenen Angeboten in unserer Akademie. Gerne beraten wir Sie, welches das optimale Training für Sie ist.
- Bereits zertifizierte SPCs müssen den SAFe® 5.0 Upgrade-Lernplan absolvieren und die SAFe® 5.0 Upgrade-Prüfung bestehen, um die SPC 5.0 Zertifizierung zu erhalten.
- Wenn Sie ein Program Consultant (SPC) 4 sind, der für den Unterricht validiert wurde, indem er die Voraussetzungen für 4.5 oder 4.6 erfüllt hat, müssen Sie auch die SAFe® 5.0 Course Delivery Enablements (CDEs) absolvieren, um für den Unterricht von 5.0-Kursen qualifiziert zu sein.
Was bedeutet SAFe® 5.0 für Unternehmen?
Für Unternehmen, die SAFe einführen möchten, kann das alles auf den ersten Blick etwas verwirrend und überfordert wirken. Das Ausmaß der Veränderungen kann da dann zunächst einmal vielleicht abschrecken. Gleichzeitig können die neuen Ideen auch genau die Dinge sein, die ein bestimmtes Team benötigt, um sich stark weiterzuentwickeln oder das neue Zielbild kann besonders anspornend wirken, weil Agilität nun ganzheitlicher gedacht wird. Für uns ist es wichtig, da ein Gefühl der Sicherheit zu vermitteln und dieses neue Big Picture als eine Vision zu sehen, an die man sich gemeinsam annähern kann. Man kann, muss aber nicht alles auf einmal anwenden. Für uns bedeutet die neue Version vor allem eine Erweiterung unseres Werkzeugkoffers, mit dem wir unseren Kunden die Erreichung ihrer Ziele ermöglichen.

![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/fileadmin/_processed_/a/8/csm_230724_Digitalisierung_9ff7a61246.jpg)
